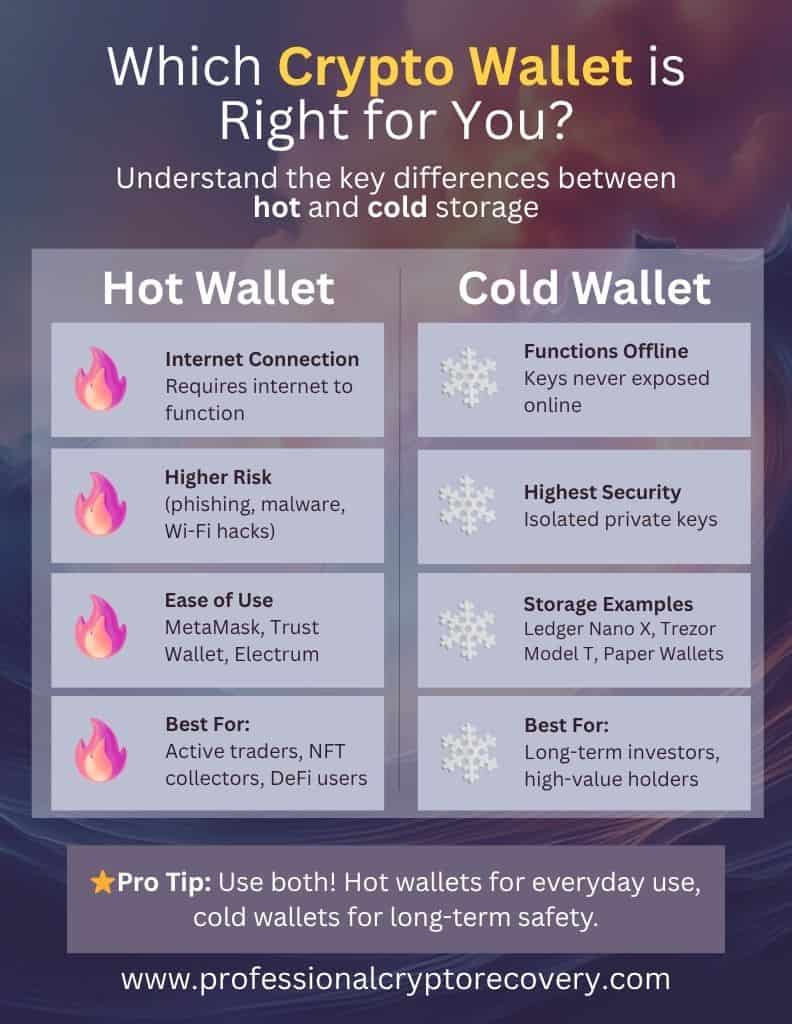
Crypto ownership begins with finding a good wallet. Depending on your goals, there are two categories: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets need to connect to the internet to work, while cold wallets do all the crucial stuff offline. The former is more convenient, while the latter is much better for security.
But security and convenience are only two of the many considerations that go into choosing a wallet. So to guide you, here is a comparison of hot and cold cryptocurrency wallets, covering everything from security and user experience to backup and recovery.
How Crypto Wallets Work
To properly distinguish hot from cold wallets, you have to understand how crypto wallets work. A real wallet holds paper money for you. But crypto is a digital currency. It has no physical form and lives entirely on the blockchain. To build a wallet for that, you need a system of keys and addresses.
Every crypto wallet has a public address. Crypto coins and tokens, on the other hand, exist as data on the blockchain. Each bit of data is associated with a particular wallet address. So when your wallet balance reads $500, it means $500 worth of assets across the blockchain are linked to your public addresses.
Your crypto wallet doesn’t contain any funds. However, it stores something just as valuable: your private keys. These prove ownership of coins associated with a wallet’s public addresses. Think of a crypto transaction as a process that requires the owner’s signature to succeed. Private keys are that signature.
So, what your crypto wallet manages are your keys, which you then use to unlock and access your assets on the blockchain. Wallets are categorized as hot or cold based on whether the keys are stored offline.
What Is a Hot Wallet
Hot wallets need an internet connection to work. You have to be online to do anything with the wallet, including signing transactions. Examples include MetaMask, TrustWallet, MyEtherWallet, and most other wallet applications out there.
Hot wallets can be categorized by platform, although many are available on multiple platforms:
1. Desktop Wallets
These are wallets that only run on desktop platforms (Windows, Mac, and/or Linux). They are installed on a PC or laptop where they store their private keys locally. You’ll have to download the installer first, but make sure you do it from the wallet’s official website to protect yourself from phishing.
Examples are Electrum, Exodus, Bitcoin Core, Rabby Desktop, and Atomic Wallet.
2. Mobile Wallets
These are wallet applications available on smartphones and tablets. Examples include Trust Wallet, MetaMask Mobile, MyEtherWallet, Rabby Mobile, and many others. Depending on your device, mobile wallets can be found on the Play Store or App Store.
3. Browser Wallets
Desktop applications aren’t the only way to manage crypto on a computer. There are lightweight wallet applications you can add to your browser, which is convenient if you’re a regular in the decentralized finance (DeFi) scene.
Examples are MetaMask, Rabby Wallet, TronLink, and Trust Wallet Extension.
Overall, these wallets are united by the fact that they store private keys in an environment with network access. But they don’t store your keys in raw format, as that would be too risky.
Once a hot wallet generates private keys, it encrypts them before storing them locally on the smartphone, desktop, or browser. The encryption key is usually derived from the PIN, password, or passphrase you set and/or biometric data.
During a transaction, the wallet software creates an unsigned transaction, signs it on the same device, and broadcasts it to the network.
What Is a Cold Wallet
Cold wallets let you manage crypto while keeping your private keys offline. Some parts of the process may happen online, but your keys stay in an isolated, secure environment that is never exposed to the internet. There are two types of cold storage:
1. Hardware wallets
A hardware wallet is a small device, usually resembling a thumb drive, that lets you generate and manage public-private key pairs. It cannot access the internet and must be connected to a phone or computer when in use. Even then, however, your keys don’t leave the device.
Here is how it works:
- You prepare a transaction on a companion app on a phone or computer that is online.
- The app sends the unsigned transaction to the hardware wallet, which is offline and has the private keys.
- The cold wallet signs the transaction internally before sending it back to the online device.
- The online device broadcasts the signed transaction to the network.
Popular hardware wallet manufacturers include Ledger (Nano S Plus, Nano X, Flex, and Stax), Trezor (Model One, Model T, Safe 5, and Safe 3), and Keystone.
2. Paper wallets
Before hardware wallets, crypto owners would create paper wallets for cold storage. This process involves using a paper wallet generator to generate public-private key pairs and printing them on paper. You must use an air-gapped computer and printer to ensure the keys are never exposed during generation or printing.
The public address is used to receive crypto, just like any other wallet, but you must manually import the private keys into a software wallet to spend funds. Most paper wallet generators provide a QR code that makes this process smoother.
Hot vs Cold Wallet Battle
Security
Security is a crucial aspect of your crypto experience. And crypto wallets, whether hot or cold, come with plenty of security. Ultimately, though, cold wallets offer the most security by ensuring your private keys never go online.
This works because anything that is online can be hacked. When a wallet is ‘hot,’ a single vulnerability — be it a compromised computer, malicious browser extension, or insecure public Wi-Fi network — can expose your private keys to an attacker during signing.
This matters because private key compromises account for the largest share of stolen crypto. According to Chainalysis, of the $2.2 billion stolen in crypto hacks in 2024, about $963 million (43.8%) resulted from compromised private keys. Notable incidents include:
- DMM Bitcoin Hack: On May 30th, 2024, attackers exploited a vulnerability in DMM Bitcoin’s private key management protocol to siphon approximately $305 million in Bitcoin from a single hot wallet.
- WazirX Hack: Just two weeks after the DMM hack, India’s largest crypto exchange, WazirX, was hit. Hackers compromised one of the exchange’s multisignature hot wallets and stole around $235 million in Ether (ETH), Shiba Inu (SHIB), and other tokens.
Cold storage eliminates this risk by isolating your keys from the internet. Every transaction is signed in a secure, offline environment, eliminating any channel for remote attackers to exploit. Even if your computer is infected with spyware, the keys remain locked in a separate platform.
This makes cold storage much more difficult to hack remotely. Something like a paper wallet is practically impossible to hack. Nonetheless, you still have some security responsibilities, like protecting your wallet from theft and damage and securing your seed phrase.
User Experience
Ease of use is in a constant tug-of-war with security. Many crypto users have to strike a balance between the two because of the number of transactions they perform. Having network access may introduce some security risks, but it’s more convenient.
Take a hardware wallet, for example. You have to connect it to your phone or computer, power it up, use an application, and manually sign the transaction on the wallet. Similarly, any private keys on a paper wallet need to be imported before you can transact your assets.
As a result, cold storage is not ideal for regular transactions. That is the domain of hot wallets. These wallets store private keys locally on your phone, PC, or browser. You only have to open the wallet application to initiate and sign a transaction. No external devices or key imports required.
The wallet software will sign the transaction and broadcast it to the network. This fast and seamless process makes hot wallets suitable for frequent use. They are overwhelmingly used in DeFi, where most enjoy good integration with exchanges, NFT marketplaces, bridges, and other DeFi platforms.
Backup and Recovery
Backup and recovery largely follow the same model for hot and cold wallets. Depending on your wallet, you get 12-24 words that you’re required to record and store securely. This is your recovery phrase. It backs up your keys, allowing you to recover your accounts if you lose access to your wallet.
You can recover your hardware wallet accounts on hot wallets and vice versa. Say you lose your Ledger Nano S and want to see if your funds are still there. You don’t have to buy a new hardware wallet. There is also the ability to import your BIP-39 seed into Trust Wallet (as one example) and immediately see the same addresses and balances.
You can also recover your hot wallet on a hardware wallet. Ledger models support restoring Trust Wallet accounts, while Trezor supports restoring Metamask, Electrum, and Exodus accounts.
Who Should Use a Cold Wallet?
Cold storage is all about absolute security. So, if you have a large quantity of assets that you want to hold long term in the safest way possible, a hardware wallet is for you. Paper wallets are also an option, albeit an outdated and less safe alternative due to how easy it is to damage paper.
Here’s a quick look at some highly rated hardware wallet models.
- Ledger Nano X: An advanced Bluetooth-enabled hardware wallet for iOS, Android, and Desktop. It supports over 5,500 coins and tokens with storage for around 100 apps. It is priced at $149.
- Trezor Model T: A feature‑rich cold wallet with a color touchscreen, USB‑C connection, and microSD slot. Costing $129, it offers top‑tier security via open‑source firmware while supporting thousands of assets. It can also serve as a hardware authenticator and digital ID device.
- Ledger Nano S Plus: Ledger’s entry-level wallet that supports over 5,500 tokens. Designed to connect via USB, it lacks Bluetooth or NFC. It is priced at $79, offering a reliable, cost-effective entry into hardware-backed security.
Who Should Use a Hot Wallet?
Hot wallets are all about convenience and ease of use. If you make regular transactions or are active in DeFi, a software wallet will serve you well. There are many options to choose from. So, make sure to pick one that is reliable and compatible with whatever ecosystems you’re active in.
Some highly rated options are:
- Electrum (Bitcoin Wallet): A lightweight, non-custodial Bitcoin wallet available on desktop and mobile. It boasts fee customization, Lightning Network support, and multisignature accounts among other features, making it a highly trusted platform.
- MetaMask (DeFi Wallet): Providing a browser extension and mobile app, MetaMask is the most widely used DeFi gateway. It allows convenient access to a vast ecosystem on Ethereum, Layer 2 networks, and other EVM-compatible chains.
- Bitcoin Core (Core Wallet): Bitcoin Core is the official full-node Bitcoin wallet and reference implementation. It fully validates blocks, stores the entire blockchain, and ensures maximum security and privacy. It is ideal for advanced users willing to dedicate storage and CPU resources.
Crypto Hot vs. Cold: Which Temperature Is Right for You?
Crypto wallets can be categorized as hot or cold based on whether or not they connect to the internet. Hot wallets need to be online to work, while cold wallets store their private keys in an isolated, offline environment.
Cold storage is generally considered better for security because it protects your wallet from remote hackers. So, if you want to hold your assets long term, it is a better alternative. Nonetheless, isolating private keys from the internet comes at the cost of usability, especially if you conduct regular transactions.
Hot wallets are better suited for everyday use. This is because storing private keys locally while being online makes conducting transactions and participating in DeFi more convenient. So if you plan on conducting transactions often, hot storage is the better option.
Ultimately, whether you’re using a cold or hot wallet, you are responsible for backup and recovery. This means setting a strong PIN, password, or passphrase and securing your seed phrase. And since we’re discussing non-custodial wallets, you may need help from a recovery expert if you lose access to yours.
At Professional Crypto Recovery, we offer affordable crypto recovery services for hardware, paper, and software wallets. With more than 20 years in IT, we have the skills, experience, and tools required for effective crypto recovery. Contact us to learn more.

Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a cold wallet and a hot wallet?
A cold wallet is a crypto storage platform that keeps your private keys disconnected from the internet and safe from hacks. A hot wallet, on the other hand, is connected to the internet, making it more convenient for frequent use but more vulnerable to cyber threats.
Is a cold wallet safer than a hot wallet?
Yes. Cold wallets offer superior security because they keep your private keys offline. This goes a long way in protecting assets from phishing, malware, and online breaches, making them ideal for long-term holding. Hot wallets come with increased risk due to constant internet exposure.
Who should use a cold wallet?
Cold wallets are best suited for investors holding large amounts of cryptocurrency for extended periods. They offer long-term security but require more effort to access funds. Traders or users who don’t need constant access to their crypto benefit the most from cold storage.
Can I use both a cold and a hot wallet?
Absolutely. Many investors use hot wallets for daily transactions and cold wallets for storing large balances. This hybrid approach balances convenience with security, allowing users to manage crypto safely while maintaining easy access to smaller, regularly used funds.
What happens if I lose my cold wallet?
If you lose your cold wallet, you can still recover your funds using the backup recovery phrase or private keys, as long as you have them securely stored. Without these, your funds could be lost permanently, making secure backups critical in cold wallet use.
